The world of 3D visualization is rapidly evolving, with holographic technology and 3D light field displays revolutionizing how we perceive and interact with digital content. While both technologies offer stunning visual experiences, they differ significantly in their methods and applications.
This article dives deep into the differences between holograms and light field technology, emphasizing their role in naked-eye 3D displays.
What Is 3D Light Field Technology?
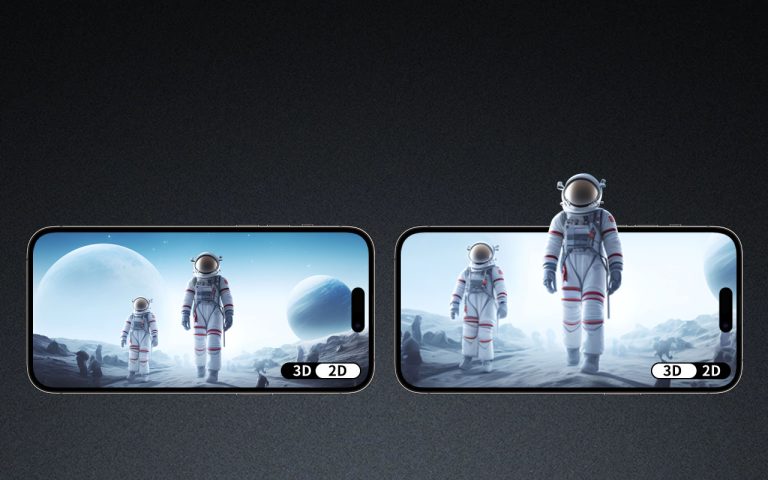
Light field technology takes a different approach to 3D imaging. It captures the direction, intensity, and color of light rays within a scene, enabling the recreation of a visual experience that changes with the viewer’s perspective. Unlike holograms, 3D light field displays are designed for natural viewing without the need for special glasses or headsets.
Light field systems utilize an array of micro-lenses or advanced computational methods to generate images. This process captures multiple viewpoints of a scene, allowing users to perceive depth and interact with the display from different angles seamlessly.
Light field technology can be applied to:
Naked-Eye 3D Displays: Light field technology excels in creating 3D visuals that are viewable without additional devices.
Medical Imaging: It provides surgeons with detailed, interactive visuals of anatomical structures.

What Are Holograms and Holographic Technology?
Holograms are three-dimensional images created by recording and reconstructing light waves. This advanced technology uses interference and diffraction to capture an image’s depth, texture, and spatial information. Holographic displays often require laser light and a medium, such as a photographic plate or digital holographic screen, to project these images.
Holographic technology is widely used in various industries, including:
Entertainment: Concerts and events leverage holograms to bring virtual performers to life.
Education: Holograms create immersive learning experiences, particularly in science and medicine.
Security: Holographic seals protect sensitive documents and currency from counterfeiting.
Despite their versatility, holograms often require specialized equipment and viewing conditions, making them less accessible for casual applications like naked-eye 3D displays.
Comparing Holograms and Light Field Technology
To better understand the differences between these two technologies, let’s compare their features, benefits, and limitations:
| FEATURE | HOLOGRAM | LIGHT FIELD TECHNOLOGY |
| Viewing Requirements | Requires lasers or special equipment | Viewable with the naked eye |
| Image Generation | Based on interference and diffraction | Captures light rays from multiple angles |
| Interactivity | Limited interactivity | Highly interactive, changes with perspective |
| Applications | Entertainment, security, education | Naked-eye 3D, AR/VR, medical imaging |
| Accessibility | Often requires specific environments | Highly accessible in various settings |
Summary
Both holograms and 3D light field technology have transformed 3D visualization, each with unique capabilities and applications. Holograms provide impressive depth and realism, often in controlled environments. Meanwhile, light field technology offers a groundbreaking approach to naked-eye 3D experiences, making it ideal for accessible and interactive applications.
As the demand for naked-eye 3D grows, 3D light field technology emerges as a frontrunner, bridging the gap between innovation and practicality. Whether in medical imaging, AR/VR, or entertainment, it paves the way for immersive, futuristic visuals without the constraints of traditional viewing equipment.
By understanding these technologies, businesses and consumers alike can harness the full potential of 3D displays to create impactful, engaging experiences.