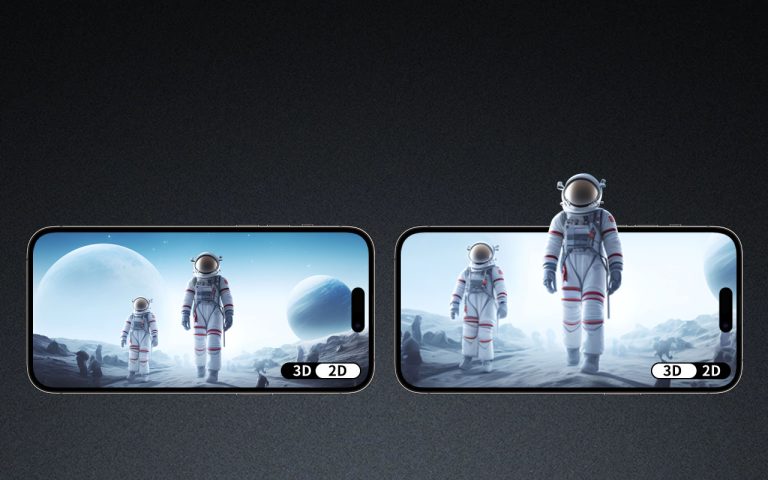
Glasses-free 3D technology (also known as autostereoscopic 3D) is a technology that has the potential to change the way we experience visual content. This technology allows viewers to perceive depth and three-dimensional effects without the need for special glasses or headphones. In this blog, we will take you back to the development and innovation of glasses-free 3D technology.
Early Beginnings
The concept of 3D visualization can be traced back to the early 19th century, In 1838, Charles Wheatstone, a British scientist and inventor, made a groundbreaking contribution to the field of optics by developing the first stereoscope. Wheatstone’s stereoscope ingeniously used a pair of mirrors positioned at 45-degree angles to combine two slightly different flat images, each one intended for one eye. When viewed through the stereoscope, these images merged in the viewer’s brain to form a single three-dimensional image that appeared to float in space, creating an astonishing illusion of depth and realism.
This innovative device not only captivated the scientific community and the public but also laid the groundwork for future advancements in 3D display technologies.
Evolution of 3D Technology
Early 20th century: the emergence of stereoscopic movies
In 1922, the world’s first 3D movie, The Power of Love, was released in Los Angeles, USA. Audiences experienced the stereoscopic effect by wearing red and blue glasses. This marked the birth of 3D movies.
Mid-20th century: Polarized 3D technology
In the 1950s, polarized 3D technology began to emerge, replacing the early red and blue 3D technology. Polarized 3D uses polarized filters and polarized glasses to separate the left and right eye images, providing a more natural 3D viewing experience.
Late 20th century: Liquid crystal shutter glasses
In the 1980s, liquid crystal shutter glasses (Active Shutter Glasses) technology came out. This technology uses liquid crystal shutter glasses to quickly alternately cover the left and right eyes, allowing each eye of the audience to see the corresponding image
Early 21st century: IMAX 3D and digital 3D movies
In the 2000s, the application of IMAX 3D and digital 3D technology brought 3D movies back to the public’s view. IMAX 3D uses large screens and high-resolution projection to provide an extremely shocking visual experience. Avatar (2009) became a milestone in digital 3D movies.

Different Types of Naked Eye 3D Technologies
Principle: Uses a layer of aligned cylindrical lenses to spread light at different angles, allowing each eye to see a slightly different image, thus creating a 3D effect in the brain.
Application Case: The Nintendo 3DS gaming console uses lenticular lens technology to achieve naked eye 3D display, providing a 3D gaming experience without the need for glasses.
The Nintendo 3DS, released in 2011, was a groundbreaking handheld gaming console that utilized naked eye 3D technology to provide an immersive gaming experience. The 3DS used a parallax barrier, a type of lenticular lens, to create the 3D effect without requiring special glasses. This innovation not only enhanced the gaming experience but also demonstrated the potential of naked eye 3D technology in the consumer market.
2. Parallax Barrier
Principle: Places a layer of fine striped screen (parallax barrier) in front of the display to control the angle of light entering the eyes, thereby creating a 3D effect.
Application Case: Early 3D smartphones, such as the HTC EVO 3D, used parallax barrier technology to achieve glasses-free 3D display.
Principle: Uses principles of interference and diffraction to record and reconstruct light waves, creating three-dimensional images that can be viewed from any angle without the need for specific viewing angles. Application Case: Holographic displays are widely used in museum exhibitions, such as the Natural History Museum in London, which uses holographic technology to showcase dinosaur fossils, allowing visitors to view these precious artifacts from all angles.
Conclusion
The origin and history of naked eye 3D technology showcase the remarkable progress made in visual display technology. From the early stereoscope to modern lenticular lenses, this journey highlights the continuous pursuit of more natural and immersive viewing experiences. As technology continues to evolve, the future of naked eye 3D holds even more exciting possibilities.