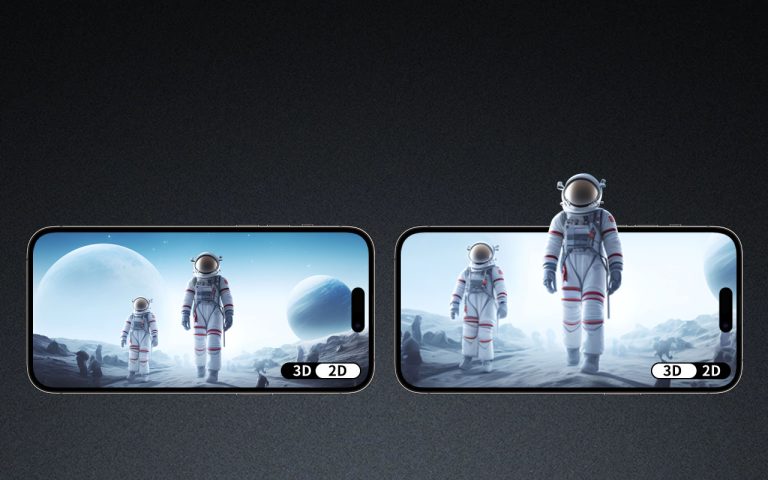
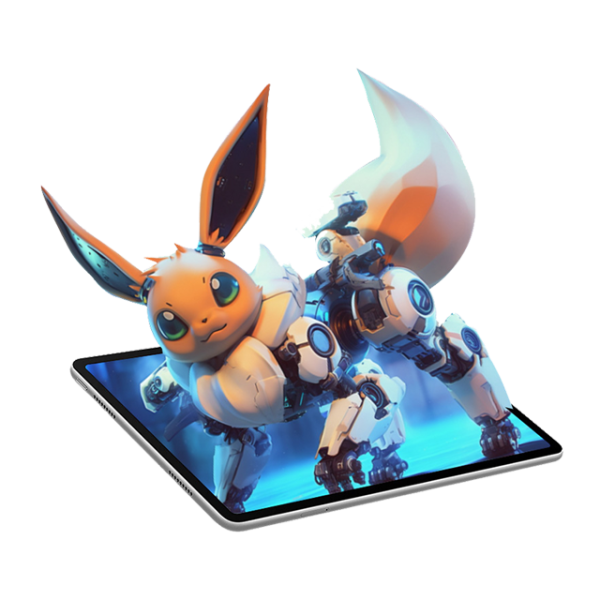
I. Introduction to lenticular lenses and their role in 3D display technology
Lenticular lenses are one of the most fundamental components in optics. They can focus light in one dimension only, whereas spherical lenses focus in all directions. This distinct capability makes lenticular lenses ideal for applications requiring precise light control, such as 3D display technology. One innovation in this field is the lenticular lens 3D system, which creates fantastic three-dimensional visuals without the need for special glasses.
II. Working Principle of Lenticular lenses
1. Structural Characteristics of Lenticular Lenses
Lenticular lenses are elongated and curved in one direction, often along their axis. This configuration makes them suitable for controlling light rays linearly and for particular distortion of images and focusing.
2. Lens Shape and Arrangement
This appears in 3D displays as lenticular lenses placed in an array and form a lenticular lens 3D configuration. This position ensures optimal alignment with the display screen, which promotes depth and clarity of the 3D effect.
III. How Lenticular Lenses Produce the 3D Effect
1. Principle of Light Refraction and Focusing
In the case of lenticular lenses, they refract the light in a way that incoming rays of light into a specific area are focused through each lens. The refraction here is pivotal for splitting light into different perspectives that are key in creating depth in lenticular lens 3D displays.
2. Perspective Separation and Image Synthesis
With these multiple views separated by lenses, each eye sees a variation of the picture. The brain uses this combined image to formulate the three-dimensional picture that gives rise to the desired 3D effect.

IV. Actualizing the 3D Effect of the Cylindrical Lens
1. Elements of the 3D Display System
Typically, a lenticular lens 3D display system contains three things: the display screenplay, a cylindrical array, and the processing unTogether, they provide authentic 3D images.
2. Superimposition of Cylindrical Lens Array on the Screen of Display
The superposition between the cylindrical array and the display screen allows one to exactly make light travel correctly during the projection of an image. Superposition between these elements is significant enough because it would project the perfect, high-definition display of a three-dimensional view.
3. Image Signal Processing and Transmission
More sophisticated image processing algorithms handle image signal synchronization and ensure smooth and seamless transmission and presentation of 3D visuals onto the display screen.
4. Presentation of the 3D Effect
Stereoscopic image generation and Display: The projection system produces at least two different images from perspective angles, where the lenticular lenses project to zones of view in the screen.
Viewing Angle and Depth Perception: The position of the viewer in front of the display determines the perceived depth and clarity of the 3D effect, hence the importance of accurate lens alignment.
V. Conclusion
The lenticular lens 3D technology represents an important milestone for naked-eye 3D display systems. In fact, through innovative cylindrical lens designs combined with leading-edge signal processing, it’s possible to present immersive, stereoscopic views in the absence of supplemental eyewear. With increased interest in glasses-free 3D viewing, the lenticular lens 3D display holds promise for greater expansion into the realm of entertainment and advertising, as well as a wide variety of other uses.