In the rapidly evolving world of consumer electronics, the term what is 3D curved display has become increasingly prevalent. Whether seen in premium smartphones, cutting-edge televisions, or high-end monitors, 3D curved displays represent a fusion of aesthetic design and advanced technology. But what is 3D curved display in a technical sense, and why is it shaping the future of visual experiences? This article delves into the definition, components, fabrication process, and implications of 3D curved displays, offering a comprehensive exploration for both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals.
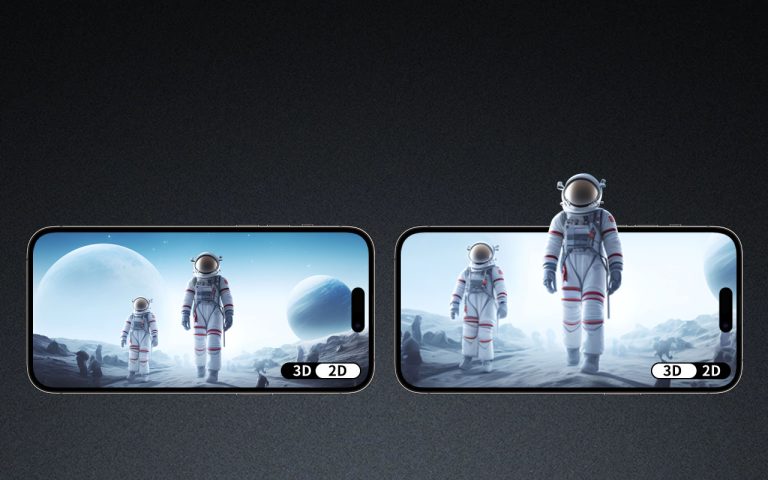
A 3D curved display is a type of electronic display panel that is physically bent or curved along one or more axes to create a three-dimensional visual effect. Unlike flat displays, these screens offer an immersive viewing experience by mimicking the natural curvature of the human eye’s field of vision.
From a technological standpoint, a 3D curved display does not inherently produce 3D images (as in stereoscopic 3D), but rather presents a curved surface that enhances depth perception, reduces image distortion, and improves viewing angles. For instance, a 1000R curvature screen, where “R” stands for the radius of curvature in millimeters, closely aligns with the average human field of vision, enhancing the sense of immersion.
Benefits of 3D Curved Displays
- Improved Immersion: The curvature makes peripheral vision more engaging, especially in gaming and cinematic applications.
- Reduced Glare and Reflection: The curved surface redirects ambient light, minimizing screen glare.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Devices with 3D curved displays often look sleeker and more modern.
What Hardware Structures does the 3D Curved Display Include?
Understanding what is 3D curved display requires an analysis of its underlying hardware. A 3D curved screen is not a single unit but a complex integration of several high-precision components. Below are the primary hardware layers involved:
Flexible OLED or AMOLED Panel
These panels are essential due to their pliable nature. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED) panels can be fabricated on flexible substrates such as polyimide, allowing them to bend without cracking. These panels are usually only 100–200 micrometers thick.
Curved Glass Substrate
The outermost layer is made from chemically strengthened curved glass, often using Gorilla Glass or similar high-durability materials. The curvature is precisely engineered to specific radii, such as 1500R or 1800R.
Touch-Sensitive Layer
Beneath the display lies a capacitive touch layer, which must also be flexible and capable of maintaining accuracy even when bent. This layer usually employs nanowire or metal mesh technology.
Polarizers and Filters
Curved displays require customized polarizer films that conform to the curvature while maintaining light control and color integrity.
Driver ICs and Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs)
To accommodate the curved form factor, the display’s driving electronics are mounted on FPCBs, which can bend without breaking the electrical pathways.

How is the “Curved” Effect Achieved in a 3D Curved Display?
To fully answer what is 3D curved display, we must explore the manufacturing techniques that enable the “curved” feature. The process is both scientifically intricate and technologically demanding.
Material Selection and Pre-treatment
- Use of polyimide substrates for OLED layers to permit bending.
- Glass sheets are ion-tempered to enhance flexibility and fracture resistance.
Thermal Forming Process
The curvature is formed through a process called thermal bending, in which display components are gradually heated to a specified temperature (typically 300–600°C) and then molded to the desired shape using precision molds.
Laser Etching and Alignment
Precision laser tools ensure the layered components are cut and aligned perfectly. Deviations over 10 microns can cause touch inaccuracy or pixel deformation.
Optical Bonding
After shaping, the individual layers are optically bonded using liquid optically clear adhesives (LOCA), which fill any gaps and eliminate air bubbles. This process preserves image clarity and touch sensitivity.
Extended Applications and Industry Impact of 3D Curved Displays
The application of 3D curved displays goes far beyond smartphones. Here are some fields where this technology is making an impact:
Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones like Samsung Galaxy S and Huawei Mate series use 3D curved screens for enhanced aesthetics and usability.
- TVs with curved displays create a more natural field of view, especially in large screens (55 inches and above).
Automotive Displays
In-vehicle infotainment systems are increasingly adopting 3D curved displays to blend seamlessly with the dashboard while providing better visibility and UX.
Gaming Monitors
Curved gaming monitors, especially those with 1000R curvature, offer an immersive experience that improves reaction time and reduces eye strain.
Summary
To summarize, what is 3D curved display refers to an advanced visual interface that combines a flexible OLED or AMOLED panel, curved glass, and integrated touch systems into a single, ergonomically designed structure. By bending the display surface, it enhances immersion, minimizes glare, and aligns with the viewer’s natural vision.
As of 2025, the global market share for curved displays is projected to reach over $20 billion, with continuous innovations in flexible electronics and transparent materials further pushing the boundaries. With 8K resolution support, higher refresh rates (up to 240Hz), and improved thermal management, the evolution of 3D curved displays is just beginning.