Creating content that can be displayed on 3D devices is a skill that increasingly intersects with digital design, computer graphics, and immersive media production. As the popularity of glasses-free 3D tablets, stereoscopic monitors, and VR/AR headsets continues to grow, the demand for high-quality, optimized 3D content has expanded across industries from entertainment to medicine. This article explores how to produce effective content for 3D devices, focusing on key techniques, tools, and considerations for optimal performance and visual fidelity.
Understanding 3D Devices and Their Content Requirements
What Are 3D Devices?
3D devices are hardware platforms capable of displaying content in three dimensions, offering depth perception through various technologies:
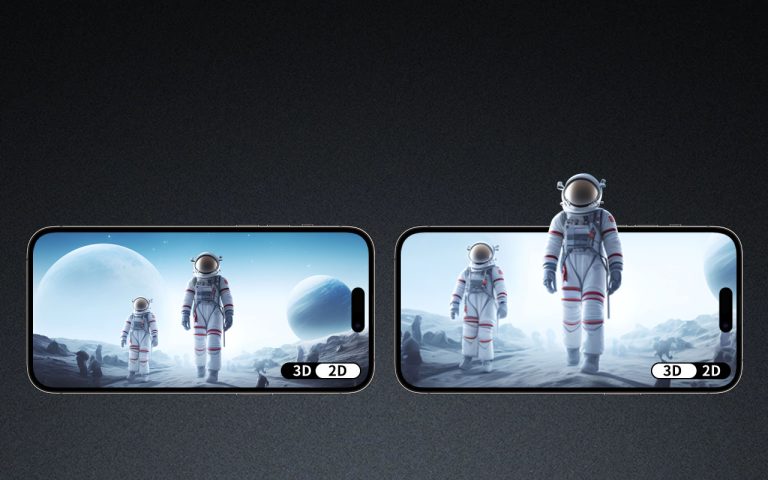
- Stereoscopic displays: Use two slightly offset images to simulate binocular vision.
- Autostereoscopic displays: Like glasses-free 3D screens, use lenticular lenses or parallax barriers.
- VR/AR headsets: Render real-time 3D environments with positional tracking.
Each type of device requires content formatted in specific ways, with resolutions ranging from 1920×1080 (for mobile glasses-free displays) to 4K per eye in high-end VR systems. Refresh rates often exceed 90 Hz in immersive setups to ensure comfort.
Essential Principles of Content Creation for 3D Devices
To craft content suitable for 3D devices, several foundational principles must be followed:
1. Depth Budget Management
The “depth budget” is the range between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene. For human comfort, it is generally recommended to keep this budget within 1%–3% of the screen width. Excessive depth can lead to:
- Eye strain
- Image doubling (ghosting)
- Difficulty focusing
Content creators must strategically manage foreground, midground, and background placement to maintain realism without discomfort.
2. Correct Stereo Pair Generation
For stereoscopic and autostereoscopic displays, every scene needs a left-eye and right-eye image pair. These must be:
- Rendered using accurate camera interaxial distances (usually 6.5 cm, the average human IPD)
- Aligned and rectified to prevent vertical disparity
- Output in a format compatible with the target device (e.g., side-by-side, top-bottom, or multi-view)
3. Frame Rate and Performance Considerations
For 3D devices, especially in VR, content must maintain high frame rates. A drop below 60 FPS can break immersion and even cause nausea. Best practices include:
- Optimizing 3D models to keep polygon counts low (e.g., <50,000 per scene for mobile)
- Using Level of Detail (LOD) techniques
- Compressing textures efficiently (e.g., DXT5 or ETC2 formats)

Tools and Software for 3D Content Creation
Content for 3D devices can be created using a variety of software tools, depending on the complexity and type of media:
1. 3D Modeling & Animation
- Blender (free, supports stereo cameras and depth maps)
- Autodesk Maya / 3ds Max
- Cinema 4D (popular for motion graphics)
2. Game Engines
- Unity: Widely used in VR/AR, supports stereo rendering and XR pipelines
- Unreal Engine: Known for photorealistic rendering, great for cinematic 3D scenes
3. Video and Post-production
- Adobe After Effects: With stereoscopic plugins for 3D composition
- DaVinci Resolve: For editing stereo footage and color grading
- Mistika VR: Specialized in 360° stereoscopic content
Adapting 2D Content for 3D Devices
If starting from 2D assets, creators can repurpose content for 3D devices by:
- Depth Mapping: Assigning depth layers and generating disparity for stereo pairs
- Parallax Animation: Creating 2.5D effects by separating image layers and animating them in space
- AI Conversion Tools: Using machine learning to automate 2D-to-3D conversion (though not always perfect)
For example, a 2D image with layered depth can be transformed using Adobe After Effects with 3D camera layers or using AI-based services like NVIDIA’s 3D Photo Reconstruction.
Quality Testing and Compatibility Checks
Testing on Multiple Devices
Always test content on various 3D devices to ensure visual integrity:
- Parallax barrier tablets (e.g., Leia Lume Pad)
- VR headsets (Meta Quest, Pico, etc.)
- 3D TVs or projection systems
Each device may render parallax, depth, or resolution differently, so testing across hardware types helps ensure a consistent experience.
Compliance and Standards
Ensure content meets current technical specifications:
- MPEG-4 MVC (Multiview Video Coding) for 3D video
- OpenXR or WebXR standards for cross-device compatibility
- glTF format for efficient real-time 3D asset delivery
Future Trends in 3D Content Creation
With advances in spatial computing and AI, the process of creating for 3D devices is becoming more automated and accessible. Future trends include:
- Real-time AI-assisted 3D modeling
- Volumetric video capture for hyperrealistic 3D
- Cloud-based rendering pipelines
By 2027, the global market for 3D display devices is expected to surpass \$200 billion, highlighting the growing importance of skilled content creation in this space.
Conclusion
Creating content for 3D devices involves a combination of artistic creativity, technical precision, and an understanding of human visual perception. Whether you’re developing interactive VR experiences or cinematic stereo video, adherence to depth principles, format standards, and performance constraints is essential. As more industries integrate 3D devices into daily use, mastering these techniques will become a vital asset for digital creators worldwide.