How Lenticular Lens Technology Enables Glasses-Free 3D
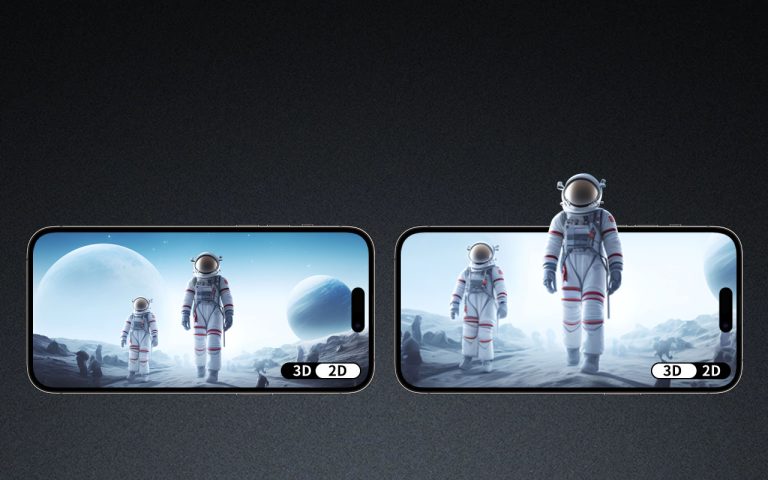
The core of glasses-free 3D display technology using lenticular lenses lies in parallax control. A lenticular lens is a transparent sheet made up of multiple tiny lenticular lenses aligned vertically or horizontally. These lenses direct light from the underlying display to each eye independently, delivering two slightly different images simultaneously—just as our eyes perceive depth in the natural world.
This separation of the left-eye and right-eye images creates the illusion of three-dimensional depth without the need for special glasses. The lenticular surface bends the light in a controlled direction, ensuring that each eye only receives the intended perspective. This optical trickery works especially well when the viewer is positioned at the correct angle or distance from the display, making proper alignment of lens pitch and image interlace critical.
Structural Characteristics of a Lenticular Lens
A lenticular lens is not merely a piece of plastic with grooves—it’s a precision optical component that requires detailed calibration. Several key structural features define its performance:
-
Lens Pitch: The distance from the center of one lens to the next. A smaller pitch allows for finer resolution but is harder to manufacture with precision.
-
Lens Radius and Curvature: These define how strongly the lens bends light. A more curved lens can create more dramatic parallax but risks distortion.
-
Orientation (Vertical or Horizontal): Vertical lenticules are more common in 3D applications, as they align with the eyes’ natural horizontal separation.
Each of these factors must match the intended viewing distance, screen resolution, and image interlacing design. Improper alignment or optical mismatch will result in ghosting or visual artifacts.
Advantages of Using Lenticular Lenses in 3D Displays
The use of lenticular lenses offers a number of practical and performance-oriented benefits in 3D display systems: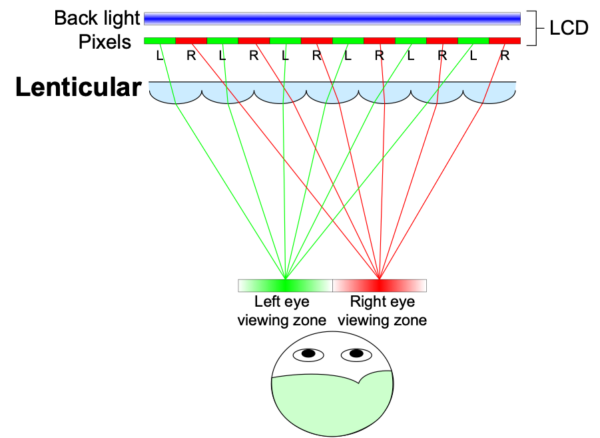
-
No Need for Wearables: Eliminates dependency on active or passive glasses, making the experience more natural and user-friendly.
-
Energy Efficient: Unlike autostereoscopic displays that use eye-tracking systems, lenticular lenses don’t require active components, making them more power-efficient.
-
Cost-Effective Scaling: Once the lenticular sheet is correctly designed, it can be mass-produced and applied to large-format displays with minimal additional cost.
-
Durability and Versatility: Lenticular sheets are generally robust and can be layered over various types of digital displays, from LED walls to smaller LCD panels.
These features make lenticular lens-based displays especially attractive for commercial settings like advertising, exhibitions, and public information systems.
Lenticular Lens Design Challenges and Optimization Techniques
Creating a visually compelling 3D experience isn’t just about slapping a lens sheet on a screen. Several critical challenges need to be addressed:
-
Image Interlacing Precision: The displayed content must be specially processed and interlaced to align with each lenticular lens. Any mismatch can result in blurry or doubled visuals.
-
View Angle Optimization: The wider the view angle, the more complex the lens design. Designers must often balance between viewing range and image clarity.
-
Moire and Ghosting Control: Moire patterns and ghosting artifacts are common issues, especially on high-resolution displays. These can be mitigated through precise calibration of the lenticular lens and image spacing.
Professional display developers often use optical simulation software and testing environments to fine-tune these variables before finalizing a lenticular design.
Use Cases Driving Demand for Lenticular Lens 3D Technology
Rather than looking at generic “applications,” it’s more useful to understand why certain sectors prefer lenticular lens solutions over other 3D display methods:
-
Retail & Advertising: Digital signage equipped with lenticular lenses grabs attention by creating motion and depth without extra hardware.
-
Museums & Exhibits: Glasses-free 3D allows multiple viewers to engage simultaneously with historical reconstructions or educational visuals.
-
Gaming & Entertainment: Handheld gaming consoles and arcades have started exploring lenticular-based displays for immersive user experiences without the hassle of accessories.
-
Medical Imaging & CAD: 3D visualizations in surgery planning or design reviews can benefit from lenticular depth cues, aiding professionals without overwhelming them with hardware.
The unique feature of delivering multi-view images without physical burden or significant energy consumption gives lenticular lens displays a clear edge in these fields.
Conclusion
The magic behind glasses-free 3D displays is not magic at all—it’s the result of meticulous engineering and the intelligent use of lenticular lens structures. By leveraging the directional control of lenticular lenses, manufacturers can offer three-dimensional visuals that feel natural, immersive, and unobtrusive.