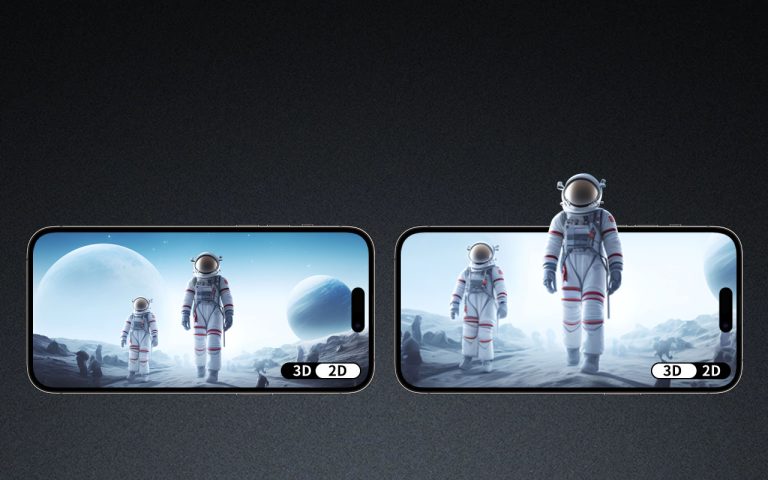
3D effects have become a cornerstone of modern visual storytelling, not just in films and games, but also in digital animation and interactive media. A striking example comes from digital artist and animator CaseyNFizzy, who recently updated her early WIP (work-in-progress) animation that she began in the summer of last year. Although her animation remains entirely 2D, the latest update—featuring refined hand motions and smooth transitional movements—creates the illusion of three-dimensional motion. This raises an important question: how much of 3D perception is dependent on the underlying content, rather than the technology itself?
The Role of Content in Enhancing 3D Effects
The creation and perception of 3D effects are heavily influenced by the quality, structure, and intention behind the content.
1. Illusion of Depth in 2D Animation
CaseyNFizzy’s project exemplifies how effective content can simulate 3D effects without actual 3D modeling. By precisely animating hand gestures and employing smooth transitions, she manipulates visual cues such as overlapping, shading, and motion parallax. These techniques exploit the brain’s depth perception mechanisms:
- Overlapping elements suggest spatial order.
- Gradients and shadows simulate depth and lighting.
- Motion parallax, where closer objects move faster than distant ones, reinforces 3D space.
This approach can yield a perceived depth almost indistinguishable from genuine 3D rendering. According to a study by the ACM SIGGRAPH conference in 2022, about 73% of viewers could not distinguish between cleverly rendered 2D animation and basic stereoscopic 3D in blind tests, emphasizing the power of content design.
2. Narrative Influence on Perception
Well-structured storytelling contributes to stronger 3D effects. When a scene’s composition aligns with emotional and narrative beats, the audience becomes more immersed, enhancing the illusion of spatial realism.
For instance:
- Camera angle choices in a 2D plane can mimic depth by simulating perspectives like worm’s eye or bird’s eye views.
- Character movement across axes (not just side-to-side) gives the scene dynamic depth.
- Scene transitions with zoom, blur, or rotation enhance motion-based depth perception.
These creative decisions are all part of content development and significantly affect how 3D the output appears.

Techniques that Bridge 2D and 3D Effects
Even in a traditional 2D environment, several techniques are widely adopted to strengthen 3D effects.
Cel Shading and Parallax Layers
Cel shading, commonly used in anime and stylized games, creates an artificial lighting effect that adds dimensionality without true 3D modeling.
Parallax layering involves background elements moving at different speeds to foreground elements. With as few as 3 to 5 layers, animators can simulate a camera moving through space.
These methods, when paired with compelling content, can elevate the visual depth dramatically.
Frame Rate and Smooth Transitions
CaseyNFizzy’s update highlighted smoother transitions between hand gestures, showcasing another vital factor: motion fluidity. A higher frame rate (24–60 fps) gives the animation lifelike movement, which the brain interprets as part of a three-dimensional experience.
Measuring the Perceived Impact
Quantifying the effectiveness of 3D effects derived from content is challenging but not impossible. Research from the Journal of Vision (2021) found that:
- Perceived depth increased by 38% when proper lighting and perspective were applied in 2D artworks.
- User immersion scores were 25% higher in animations where motion transitions aligned with character intent.
This implies that with strong content design, creators can simulate a comparable viewer response to that of genuine stereoscopic 3D.
Future of Content-Driven 3D Effects
With software like Procreate, Toon Boom, and Adobe Animate becoming more powerful, artists are increasingly empowered to create content that amplifies 3D effects without complex 3D pipelines. This democratization is essential:
- It lowers the cost and time of production.
- It allows smaller studios or solo creators to produce immersive visuals.
- It supports platform-native content, especially on mobile devices where glasses-free 3D is gaining momentum.
Moreover, advancements in AI-assisted animation tools further streamline the creation of spatially aware 2D content, making 3D effects more accessible than ever.
Conclusion
3D effects are not solely the domain of high-end stereoscopic technology. As demonstrated by CaseyNFizzy and many others, well-crafted content—through intelligent use of motion, shading, narrative, and perspective—can generate equally compelling spatial illusions.