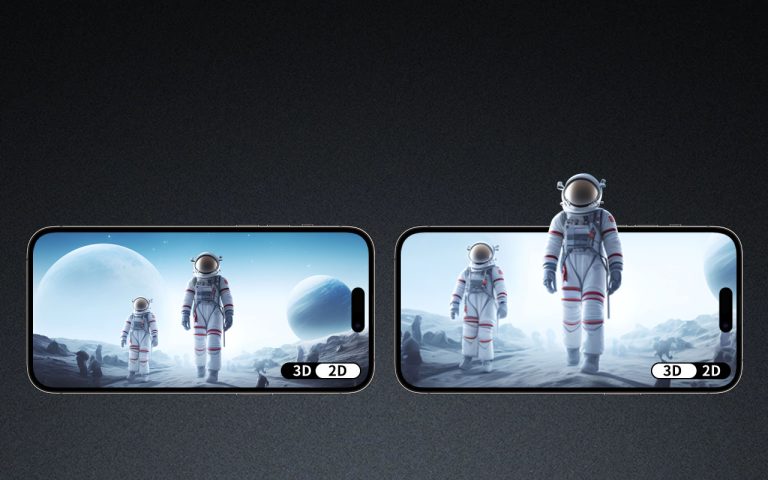
Autostereoscopic monitors, known for their ability to display 3D images without the need for special glasses, have garnered significant attention in recent years. A common question that arises among potential users is whether these advanced displays are compatible with both Windows and Mac systems. The answer to this inquiry is multifaceted and requires exploring in detail, especially considering the technical specifications and system requirements that autostereoscopic monitors entail.
Compatibility Overview: Autostereoscopic Monitor and Operating Systems
When it comes to compatibility, autostereoscopic monitors are designed to work seamlessly with a range of operating systems, including Windows and macOS. However, the extent of support can vary based on several factors, such as the monitor’s specific model, its drivers, and the operating system’s version.
 1. Windows System Compatibility
1. Windows System Compatibility
Windows systems, particularly from Windows 7 onwards, have shown robust support for autostereoscopic technology. Most modern autostereoscopic monitors come with dedicated drivers and software that enhance compatibility with Windows. These drivers ensure that the 3D effect is rendered correctly, with minimal latency and optimal image quality. For instance, a monitor with a refresh rate of 120Hz and a resolution of 1920×1080 is likely to perform exceptionally well on a Windows 10 system, provided the necessary drivers are installed.
Moreover, Windows offers extensive customization options, allowing users to tweak settings for optimal 3D viewing. This level of control is crucial as autostereoscopic displays require precise calibration to achieve the desired 3D effect. With Windows, users can adjust parameters like depth perception, convergence, and separation to suit their preferences.
2. Mac System Compatibility
macOS, on the other hand, presents a slightly different scenario. While autostereoscopic monitors are compatible with Mac systems, the level of support can vary. Some monitors may require third-party software or additional drivers to function correctly on macOS. Despite this, many high-end autostereoscopic models are designed to work out-of-the-box with macOS, offering a plug-and-play experience.
A key factor to consider is the macOS version. Newer versions, such as macOS Catalina and Big Sur, tend to have better support for advanced display technologies. For example, a monitor with a 60Hz refresh rate and a resolution of 3840×2160 might work flawlessly on the latest macOS, delivering stunning 3D visuals. However, users may need to update their system software or install additional software to unlock the full potential of their autostereoscopic monitor.
Additional Considerations for Compatibility
Beyond the operating system, several other factors influence the compatibility of autostereoscopic monitors. These include:
Hardware Requirements: Both Windows and Mac systems need to meet certain hardware specifications to support autostereoscopic displays. For instance, a powerful graphics card is essential for rendering 3D images smoothly.
- Driver Updates: Regularly updating the monitor’s drivers is crucial for maintaining compatibility and performance. Manufacturers often release new drivers to fix bugs and improve compatibility with the latest operating systems.
- Software Support: Some autostereoscopic monitors come with proprietary software that enhances the 3D viewing experience. This software may need to be compatible with the user’s operating system to function correctly.
- Connectivity Options: The type of connection (HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C) can also affect compatibility. Ensuring that the monitor and the computer have compatible ports is essential for a hassle-free setup.
Industry Trends and Innovations
The global market for autostereoscopic monitors is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.5% from 2023 to 2030, driven by advancements in display technology and increasing demand for 3D visualization tools. Future developments may include higher resolutions (8K and beyond) and improved compatibility with macOS, making these monitors more accessible to a broader audience.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap Between Autostereoscopic Monitors and Operating Systems
In conclusion, autostereoscopic monitors are indeed compatible with both Windows and Mac systems, albeit with some variations in support and performance. By understanding the technical specifications, system requirements, and potential compatibility issues, users can make informed decisions when choosing an autostereoscopic monitor for their setup.
Whether you’re a Windows user or a Mac enthusiast, the world of 3D computing is within reach, thanks to the advancements in autostereoscopic technology. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect even better compatibility and performance across different operating systems in the future.