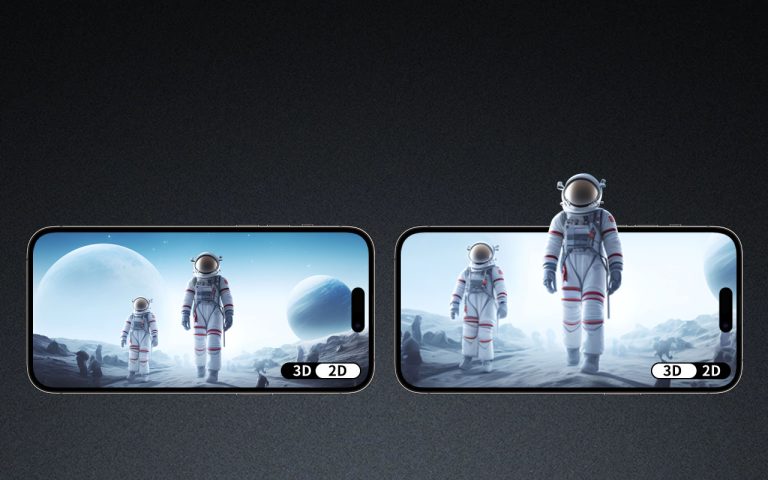
In the ever-evolving landscape of television technology, 3D TV ads have emerged as a groundbreaking way to captivate audiences. Integrating these immersive advertisements into 3D TV panels requires a meticulous approach to ensure seamless integration and maximum impact. This article delves into the technical and strategic aspects of implementing 3D TV ads within 3D TV panels, highlighting key considerations and best practices.
Understanding the Basics of 3D TV Panels
3D TV panels utilize advanced display technologies to create a three-dimensional viewing experience. These panels often employ either active shutter or passive polarized glass systems. Active shutter technology rapidly alternates between left and right-eye images, while passive systems use polarized filters to direct different images to each eye. Compatibility with these systems is paramount for 3D TV ads to shine.
Key Considerations for 3D TV Ad Implementation
Content Creation: Developing 3D content specifically for TV ads involves sophisticated software and skilled animators. The ads must maintain a consistent depth perception, ensuring viewers experience a realistic 3D effect without discomfort. A common guideline is to keep the depth budget within ±10% of the screen’s width to avoid eye strain.

1. Technical Specifications and Compatibility
Resolution and Frame Rate: 3D TV ads should ideally be rendered at a high resolution, such as 1080p or even 4K, to maintain clarity when viewed on large screens. Additionally, a frame rate of at least 60 frames per second (fps) per eye is recommended to prevent motion blur and ensure smoothness.
Encoding and Transmission: Efficient encoding formats like MVC (Multiview Video Coding) are essential for transmitting 3D content without overwhelming bandwidth. Broadcasters must ensure compatibility with existing TV infrastructure while planning for future upgrades.
2. Strategies for Effective Integration
2.1 Depth Management
Subtle Depth Effects: Avoid excessive depth to prevent viewer fatigue. A balanced approach, with objects protruding or receding by no more than a few inches, enhances the viewing experience.
Consistent Depth Cues: Maintain consistent depth cues throughout the ad to avoid confusing the viewer’s brain, which relies on these cues to interpret 3D space.
2.2 Engagement and Interactivity
Interactive Elements: Incorporating interactive elements, where viewers can engage with the ad using a secondary device, can significantly boost engagement. For instance, QR codes or augmented reality (AR) features that complement the 3D ad can drive higher interaction rates.
Storytelling Techniques: Leverage 3D storytelling techniques to create immersive narratives. Use depth to guide the viewer’s focus, enhancing the emotional impact of the ad. A study showed that 3D ads increased recall rates by up to 20% compared to 2D counterparts.
Measuring Success and ROI
Viewer Metrics: Utilize viewer metrics such as engagement time, interaction rates, and recall tests to gauge the effectiveness of 3D TV ads. These metrics provide valuable insights into how viewers perceive and respond to 3D content.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to ensure that the investment in 3D ad creation and distribution yields a positive return on investment (ROI). Consider factors like production costs, ad placement fees, and potential revenue uplift from increased viewer engagement.
Conclusion
Implementing 3D TV ads in 3D TV panels is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of content creation, technical specifications, viewer experience, and engagement strategies. By adhering to best practices and leveraging advanced technologies, broadcasters can create immersive and engaging 3D TV ads that captivate audiences and drive higher ROI. As the technology continues to evolve, the potential for 3D TV ads to revolutionize the advertising industry becomes increasingly evident.